Typical tasks
Business data analyses
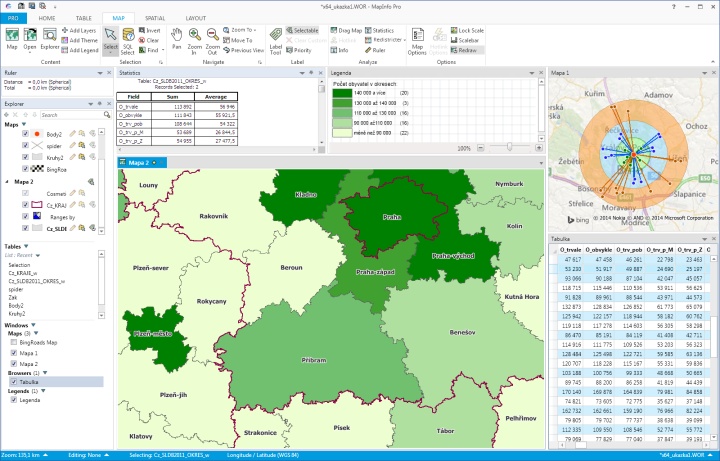
Business economical data and customer information are the most important source of internal information over which proceeds most analyzes. These analyses are base for operational and strategic planning and management.
If there is address in customer data (or geographic coordinates) it is possible to create a map layer from this database. Then you can use all the information connected to customers and clearly analyze data on a map. The analysis results will answer the following questions:
- In which areas has our company the most customers?
- Are "successful" areas specific in some way? Where can we find more of these areas?
- Why is business not successful in selected areas?
- What is the development of chosen product sale in selected areas?
- What share of the market does our company have with a specific product in different administrative regions (e.g. in municipalities or PostCode areas)?
- What is the potential of each area?
If you know about these and other similar questions the answer will be able to better respond to changing market and competitive actions.
Business territories and catchment areas
Effective distribution of regions between sales representatives of a company and optimal proposal of catchment areas for sale or service units are common task of geographical analyses. Key role is played by the right combination of all available data including historical business data of the client.
Many companies face similar tasks intuitively and thus deprive themselves of the opportunity to include more variables to their seemingly unrelated analyses. If you need to solve similar problems we would like to help you solve following tasks:
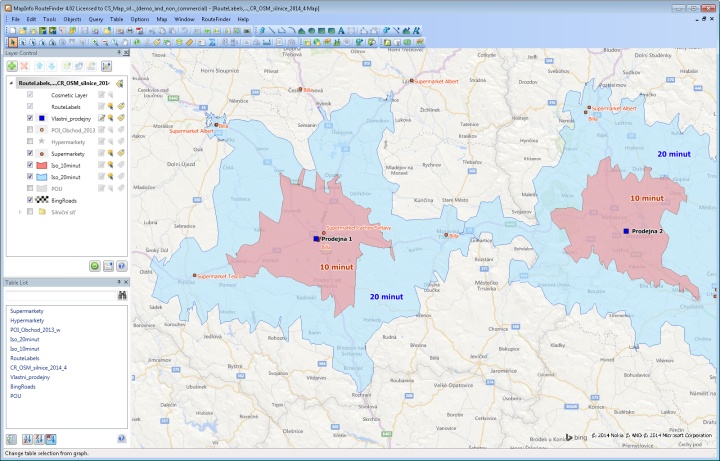
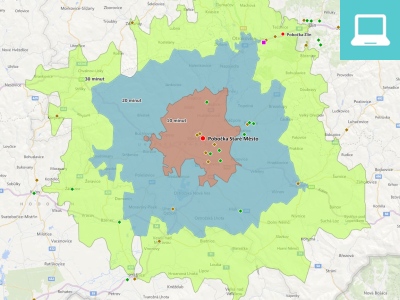
- How many residents live within driving distance X minutes from our store?
- What is the overlap of catchment areas and what is the real potential of individual stores?
- What is the optimal count of sales representatives and what regions should they have?
- How to automatically assign business event to sales representative?
- How to transparently monitor and analyze work of sales representatives?
Search of suitable locations, competition analysis
The result of wrong decision when choosing location for a new store, office or warehouse is mostly critical. Reliable and complete information is very important in the field of expansion. At the same time this information must be presented transparently and clearly.
Key task is the project preparation and implementation for the deployment of new sales units on the existing market and ongoing evaluation and analysis of the of cannibalization of existing stores. These strategies can take into account demographic characteristics, competition, shopping habits, current own stores, transport accessibility, economic growth of the region and other important parameters. Geographic analysis results will help you:
- Identify optimal locations for expansion.
- Maximize the share of the market and output per unit concurrently.
- Mitigate cannibalization between stores.
- Determine which stores to close or renovate.
- Determine potential of defined area.
Sociodemographic and sector data
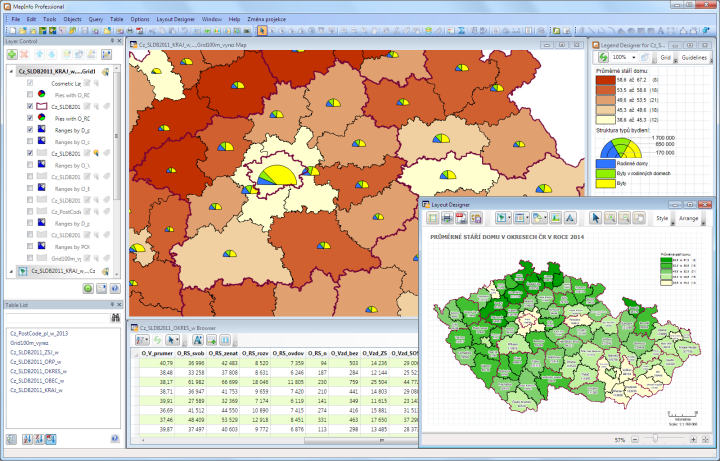
Population data is currently very important source of information for decision-making not only in the state administration but also in commercial institutions. The most famous and comprehensive data source is undoubtedly the Census that is done every 10 years.
Census data is very often supplemented by additional important information such as average salary in regions, purchasing power of the population, customer and other habits of inhabitants, population migration during the day or a wide range of sector statistics on construction, agriculture, industry etc.
GIS solutions enable you to display all these data, combine with your own data, analyze it and respond to your questions:
- Where are areas with sufficient population?
- What is the structure of population in created catchment area around the proposed locality for the construction of a new branch?
- Where are the areas with composition of residents which match the products we offer?
- Is there sufficient purchasing power of population in target area?
- Where are target companies located?
Managing of technical infrastructure
The use of GIS is an indispensable part of industrially and technically oriented companies. Waterworks, power suppliers, gas or telecommunication companies must have perfect knowledge about their facilities and be prepared to deal with critical situations on its network.
Besides standard geographical analyses is also very important the exchange ability and data compatibility between different platforms and applications especially between CAD/GIS solutions. Most often solved problems are:
- Management and maintenance of company's equipment (adding and deleting feature, changing equipment etc.).
- Critical conditions simulations (eg. how and which consumers will be affected in case of malfunction).
- Geographic visualization of the current network status etc.